02_MySQL_DQL基本语法
[email protected]:tomxwd/MySQL-Basic.git
这里是DQL(Data Query Language)
准备工作
建表;
/*
SQLyog Ultimate v10.00 Beta1
MySQL - 5.5.15 : Database - myemployees
*********************************************************************
*/
/*!40101 SET NAMES utf8 */;
/*!40101 SET SQL_MODE=''*/;
/*!40014 SET @OLD_UNIQUE_CHECKS=@@UNIQUE_CHECKS, UNIQUE_CHECKS=0 */;
/*!40014 SET @OLD_FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=@@FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS, FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0 */;
/*!40101 SET @OLD_SQL_MODE=@@SQL_MODE, SQL_MODE='NO_AUTO_VALUE_ON_ZERO' */;
/*!40111 SET @OLD_SQL_NOTES=@@SQL_NOTES, SQL_NOTES=0 */;
CREATE DATABASE /*!32312 IF NOT EXISTS*/`myemployees` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET gb2312 */;
USE `myemployees`;
/*Table structure for table `departments` */
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `departments`;
CREATE TABLE `departments` (
`department_id` int(4) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`department_name` varchar(3) DEFAULT NULL,
`manager_id` int(6) DEFAULT NULL,
`location_id` int(4) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`department_id`),
KEY `loc_id_fk` (`location_id`),
CONSTRAINT `loc_id_fk` FOREIGN KEY (`location_id`) REFERENCES `locations` (`location_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=271 DEFAULT CHARSET=gb2312;
/*Data for the table `departments` */
insert into `departments`(`department_id`,`department_name`,`manager_id`,`location_id`) values (10,'Adm',200,1700),(20,'Mar',201,1800),(30,'Pur',114,1700),(40,'Hum',203,2400),(50,'Shi',121,1500),(60,'IT',103,1400),(70,'Pub',204,2700),(80,'Sal',145,2500),(90,'Exe',100,1700),(100,'Fin',108,1700),(110,'Acc',205,1700),(120,'Tre',NULL,1700),(130,'Cor',NULL,1700),(140,'Con',NULL,1700),(150,'Sha',NULL,1700),(160,'Ben',NULL,1700),(170,'Man',NULL,1700),(180,'Con',NULL,1700),(190,'Con',NULL,1700),(200,'Ope',NULL,1700),(210,'IT ',NULL,1700),(220,'NOC',NULL,1700),(230,'IT ',NULL,1700),(240,'Gov',NULL,1700),(250,'Ret',NULL,1700),(260,'Rec',NULL,1700),(270,'Pay',NULL,1700);
/*Table structure for table `employees` */
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `employees`;
CREATE TABLE `employees` (
`employee_id` int(6) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`first_name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`last_name` varchar(25) DEFAULT NULL,
`email` varchar(25) DEFAULT NULL,
`phone_number` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`job_id` varchar(10) DEFAULT NULL,
`salary` double(10,2) DEFAULT NULL,
`commission_pct` double(4,2) DEFAULT NULL,
`manager_id` int(6) DEFAULT NULL,
`department_id` int(4) DEFAULT NULL,
`hiredate` datetime DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`employee_id`),
KEY `dept_id_fk` (`department_id`),
KEY `job_id_fk` (`job_id`),
CONSTRAINT `dept_id_fk` FOREIGN KEY (`department_id`) REFERENCES `departments` (`department_id`),
CONSTRAINT `job_id_fk` FOREIGN KEY (`job_id`) REFERENCES `jobs` (`job_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=207 DEFAULT CHARSET=gb2312;
/*Data for the table `employees` */
insert into `employees`(`employee_id`,`first_name`,`last_name`,`email`,`phone_number`,`job_id`,`salary`,`commission_pct`,`manager_id`,`department_id`,`hiredate`) values (100,'Steven','K_ing','SKING','515.123.4567','AD_PRES',24000.00,NULL,NULL,90,'1992-04-03 00:00:00'),(101,'Neena','Kochhar','NKOCHHAR','515.123.4568','AD_VP',17000.00,NULL,100,90,'1992-04-03 00:00:00'),(102,'Lex','De Haan','LDEHAAN','515.123.4569','AD_VP',17000.00,NULL,100,90,'1992-04-03 00:00:00'),(103,'Alexander','Hunold','AHUNOLD','590.423.4567','IT_PROG',9000.00,NULL,102,60,'1992-04-03 00:00:00'),(104,'Bruce','Ernst','BERNST','590.423.4568','IT_PROG',6000.00,NULL,103,60,'1992-04-03 00:00:00'),(105,'David','Austin','DAUSTIN','590.423.4569','IT_PROG',4800.00,NULL,103,60,'1998-03-03 00:00:00'),(106,'Valli','Pataballa','VPATABAL','590.423.4560','IT_PROG',4800.00,NULL,103,60,'1998-03-03 00:00:00'),(107,'Diana','Lorentz','DLORENTZ','590.423.5567','IT_PROG',4200.00,NULL,103,60,'1998-03-03 00:00:00'),(108,'Nancy','Greenberg','NGREENBE','515.124.4569','FI_MGR',12000.00,NULL,101,100,'1998-03-03 00:00:00'),(109,'Daniel','Faviet','DFAVIET','515.124.4169','FI_ACCOUNT',9000.00,NULL,108,100,'1998-03-03 00:00:00'),(110,'John','Chen','JCHEN','515.124.4269','FI_ACCOUNT',8200.00,NULL,108,100,'2000-09-09 00:00:00'),(111,'Ismael','Sciarra','ISCIARRA','515.124.4369','FI_ACCOUNT',7700.00,NULL,108,100,'2000-09-09 00:00:00'),(112,'Jose Manuel','Urman','JMURMAN','515.124.4469','FI_ACCOUNT',7800.00,NULL,108,100,'2000-09-09 00:00:00'),(113,'Luis','Popp','LPOPP','515.124.4567','FI_ACCOUNT',6900.00,NULL,108,100,'2000-09-09 00:00:00'),(114,'Den','Raphaely','DRAPHEAL','515.127.4561','PU_MAN',11000.00,NULL,100,30,'2000-09-09 00:00:00'),(115,'Alexander','Khoo','AKHOO','515.127.4562','PU_CLERK',3100.00,NULL,114,30,'2000-09-09 00:00:00'),(116,'Shelli','Baida','SBAIDA','515.127.4563','PU_CLERK',2900.00,NULL,114,30,'2000-09-09 00:00:00'),(117,'Sigal','Tobias','STOBIAS','515.127.4564','PU_CLERK',2800.00,NULL,114,30,'2000-09-09 00:00:00'),(118,'Guy','Himuro','GHIMURO','515.127.4565','PU_CLERK',2600.00,NULL,114,30,'2000-09-09 00:00:00'),(119,'Karen','Colmenares','KCOLMENA','515.127.4566','PU_CLERK',2500.00,NULL,114,30,'2000-09-09 00:00:00'),(120,'Matthew','Weiss','MWEISS','650.123.1234','ST_MAN',8000.00,NULL,100,50,'2004-02-06 00:00:00'),(121,'Adam','Fripp','AFRIPP','650.123.2234','ST_MAN',8200.00,NULL,100,50,'2004-02-06 00:00:00'),(122,'Payam','Kaufling','PKAUFLIN','650.123.3234','ST_MAN',7900.00,NULL,100,50,'2004-02-06 00:00:00'),(123,'Shanta','Vollman','SVOLLMAN','650.123.4234','ST_MAN',6500.00,NULL,100,50,'2004-02-06 00:00:00'),(124,'Kevin','Mourgos','KMOURGOS','650.123.5234','ST_MAN',5800.00,NULL,100,50,'2004-02-06 00:00:00'),(125,'Julia','Nayer','JNAYER','650.124.1214','ST_CLERK',3200.00,NULL,120,50,'2004-02-06 00:00:00'),(126,'Irene','Mikkilineni','IMIKKILI','650.124.1224','ST_CLERK',2700.00,NULL,120,50,'2004-02-06 00:00:00'),(127,'James','Landry','JLANDRY','650.124.1334','ST_CLERK',2400.00,NULL,120,50,'2004-02-06 00:00:00'),(128,'Steven','Markle','SMARKLE','650.124.1434','ST_CLERK',2200.00,NULL,120,50,'2004-02-06 00:00:00'),(129,'Laura','Bissot','LBISSOT','650.124.5234','ST_CLERK',3300.00,NULL,121,50,'2004-02-06 00:00:00'),(130,'Mozhe','Atkinson','MATKINSO','650.124.6234','ST_CLERK',2800.00,NULL,121,50,'2004-02-06 00:00:00'),(131,'James','Marlow','JAMRLOW','650.124.7234','ST_CLERK',2500.00,NULL,121,50,'2004-02-06 00:00:00'),(132,'TJ','Olson','TJOLSON','650.124.8234','ST_CLERK',2100.00,NULL,121,50,'2004-02-06 00:00:00'),(133,'Jason','Mallin','JMALLIN','650.127.1934','ST_CLERK',3300.00,NULL,122,50,'2004-02-06 00:00:00'),(134,'Michael','Rogers','MROGERS','650.127.1834','ST_CLERK',2900.00,NULL,122,50,'2002-12-23 00:00:00'),(135,'Ki','Gee','KGEE','650.127.1734','ST_CLERK',2400.00,NULL,122,50,'2002-12-23 00:00:00'),(136,'Hazel','Philtanker','HPHILTAN','650.127.1634','ST_CLERK',2200.00,NULL,122,50,'2002-12-23 00:00:00'),(137,'Renske','Ladwig','RLADWIG','650.121.1234','ST_CLERK',3600.00,NULL,123,50,'2002-12-23 00:00:00'),(138,'Stephen','Stiles','SSTILES','650.121.2034','ST_CLERK',3200.00,NULL,123,50,'2002-12-23 00:00:00'),(139,'John','Seo','JSEO','650.121.2019','ST_CLERK',2700.00,NULL,123,50,'2002-12-23 00:00:00'),(140,'Joshua','Patel','JPATEL','650.121.1834','ST_CLERK',2500.00,NULL,123,50,'2002-12-23 00:00:00'),(141,'Trenna','Rajs','TRAJS','650.121.8009','ST_CLERK',3500.00,NULL,124,50,'2002-12-23 00:00:00'),(142,'Curtis','Davies','CDAVIES','650.121.2994','ST_CLERK',3100.00,NULL,124,50,'2002-12-23 00:00:00'),(143,'Randall','Matos','RMATOS','650.121.2874','ST_CLERK',2600.00,NULL,124,50,'2002-12-23 00:00:00'),(144,'Peter','Vargas','PVARGAS','650.121.2004','ST_CLERK',2500.00,NULL,124,50,'2002-12-23 00:00:00'),(145,'John','Russell','JRUSSEL','011.44.1344.429268','SA_MAN',14000.00,0.40,100,80,'2002-12-23 00:00:00'),(146,'Karen','Partners','KPARTNER','011.44.1344.467268','SA_MAN',13500.00,0.30,100,80,'2002-12-23 00:00:00'),(147,'Alberto','Errazuriz','AERRAZUR','011.44.1344.429278','SA_MAN',12000.00,0.30,100,80,'2002-12-23 00:00:00'),(148,'Gerald','Cambrault','GCAMBRAU','011.44.1344.619268','SA_MAN',11000.00,0.30,100,80,'2002-12-23 00:00:00'),(149,'Eleni','Zlotkey','EZLOTKEY','011.44.1344.429018','SA_MAN',10500.00,0.20,100,80,'2002-12-23 00:00:00'),(150,'Peter','Tucker','PTUCKER','011.44.1344.129268','SA_REP',10000.00,0.30,145,80,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(151,'David','Bernstein','DBERNSTE','011.44.1344.345268','SA_REP',9500.00,0.25,145,80,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(152,'Peter','Hall','PHALL','011.44.1344.478968','SA_REP',9000.00,0.25,145,80,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(153,'Christopher','Olsen','COLSEN','011.44.1344.498718','SA_REP',8000.00,0.20,145,80,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(154,'Nanette','Cambrault','NCAMBRAU','011.44.1344.987668','SA_REP',7500.00,0.20,145,80,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(155,'Oliver','Tuvault','OTUVAULT','011.44.1344.486508','SA_REP',7000.00,0.15,145,80,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(156,'Janette','K_ing','JKING','011.44.1345.429268','SA_REP',10000.00,0.35,146,80,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(157,'Patrick','Sully','PSULLY','011.44.1345.929268','SA_REP',9500.00,0.35,146,80,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(158,'Allan','McEwen','AMCEWEN','011.44.1345.829268','SA_REP',9000.00,0.35,146,80,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(159,'Lindsey','Smith','LSMITH','011.44.1345.729268','SA_REP',8000.00,0.30,146,80,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(160,'Louise','Doran','LDORAN','011.44.1345.629268','SA_REP',7500.00,0.30,146,80,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(161,'Sarath','Sewall','SSEWALL','011.44.1345.529268','SA_REP',7000.00,0.25,146,80,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(162,'Clara','Vishney','CVISHNEY','011.44.1346.129268','SA_REP',10500.00,0.25,147,80,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(163,'Danielle','Greene','DGREENE','011.44.1346.229268','SA_REP',9500.00,0.15,147,80,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(164,'Mattea','Marvins','MMARVINS','011.44.1346.329268','SA_REP',7200.00,0.10,147,80,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(165,'David','Lee','DLEE','011.44.1346.529268','SA_REP',6800.00,0.10,147,80,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(166,'Sundar','Ande','SANDE','011.44.1346.629268','SA_REP',6400.00,0.10,147,80,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(167,'Amit','Banda','ABANDA','011.44.1346.729268','SA_REP',6200.00,0.10,147,80,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(168,'Lisa','Ozer','LOZER','011.44.1343.929268','SA_REP',11500.00,0.25,148,80,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(169,'Harrison','Bloom','HBLOOM','011.44.1343.829268','SA_REP',10000.00,0.20,148,80,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(170,'Tayler','Fox','TFOX','011.44.1343.729268','SA_REP',9600.00,0.20,148,80,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(171,'William','Smith','WSMITH','011.44.1343.629268','SA_REP',7400.00,0.15,148,80,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(172,'Elizabeth','Bates','EBATES','011.44.1343.529268','SA_REP',7300.00,0.15,148,80,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(173,'Sundita','Kumar','SKUMAR','011.44.1343.329268','SA_REP',6100.00,0.10,148,80,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(174,'Ellen','Abel','EABEL','011.44.1644.429267','SA_REP',11000.00,0.30,149,80,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(175,'Alyssa','Hutton','AHUTTON','011.44.1644.429266','SA_REP',8800.00,0.25,149,80,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(176,'Jonathon','Taylor','JTAYLOR','011.44.1644.429265','SA_REP',8600.00,0.20,149,80,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(177,'Jack','Livingston','JLIVINGS','011.44.1644.429264','SA_REP',8400.00,0.20,149,80,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(178,'Kimberely','Grant','KGRANT','011.44.1644.429263','SA_REP',7000.00,0.15,149,NULL,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(179,'Charles','Johnson','CJOHNSON','011.44.1644.429262','SA_REP',6200.00,0.10,149,80,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(180,'Winston','Taylor','WTAYLOR','650.507.9876','SH_CLERK',3200.00,NULL,120,50,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(181,'Jean','Fleaur','JFLEAUR','650.507.9877','SH_CLERK',3100.00,NULL,120,50,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(182,'Martha','Sullivan','MSULLIVA','650.507.9878','SH_CLERK',2500.00,NULL,120,50,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(183,'Girard','Geoni','GGEONI','650.507.9879','SH_CLERK',2800.00,NULL,120,50,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(184,'Nandita','Sarchand','NSARCHAN','650.509.1876','SH_CLERK',4200.00,NULL,121,50,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(185,'Alexis','Bull','ABULL','650.509.2876','SH_CLERK',4100.00,NULL,121,50,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(186,'Julia','Dellinger','JDELLING','650.509.3876','SH_CLERK',3400.00,NULL,121,50,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(187,'Anthony','Cabrio','ACABRIO','650.509.4876','SH_CLERK',3000.00,NULL,121,50,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(188,'Kelly','Chung','KCHUNG','650.505.1876','SH_CLERK',3800.00,NULL,122,50,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(189,'Jennifer','Dilly','JDILLY','650.505.2876','SH_CLERK',3600.00,NULL,122,50,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(190,'Timothy','Gates','TGATES','650.505.3876','SH_CLERK',2900.00,NULL,122,50,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(191,'Randall','Perkins','RPERKINS','650.505.4876','SH_CLERK',2500.00,NULL,122,50,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(192,'Sarah','Bell','SBELL','650.501.1876','SH_CLERK',4000.00,NULL,123,50,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(193,'Britney','Everett','BEVERETT','650.501.2876','SH_CLERK',3900.00,NULL,123,50,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(194,'Samuel','McCain','SMCCAIN','650.501.3876','SH_CLERK',3200.00,NULL,123,50,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(195,'Vance','Jones','VJONES','650.501.4876','SH_CLERK',2800.00,NULL,123,50,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(196,'Alana','Walsh','AWALSH','650.507.9811','SH_CLERK',3100.00,NULL,124,50,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(197,'Kevin','Feeney','KFEENEY','650.507.9822','SH_CLERK',3000.00,NULL,124,50,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(198,'Donald','OConnell','DOCONNEL','650.507.9833','SH_CLERK',2600.00,NULL,124,50,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(199,'Douglas','Grant','DGRANT','650.507.9844','SH_CLERK',2600.00,NULL,124,50,'2014-03-05 00:00:00'),(200,'Jennifer','Whalen','JWHALEN','515.123.4444','AD_ASST',4400.00,NULL,101,10,'2016-03-03 00:00:00'),(201,'Michael','Hartstein','MHARTSTE','515.123.5555','MK_MAN',13000.00,NULL,100,20,'2016-03-03 00:00:00'),(202,'Pat','Fay','PFAY','603.123.6666','MK_REP',6000.00,NULL,201,20,'2016-03-03 00:00:00'),(203,'Susan','Mavris','SMAVRIS','515.123.7777','HR_REP',6500.00,NULL,101,40,'2016-03-03 00:00:00'),(204,'Hermann','Baer','HBAER','515.123.8888','PR_REP',10000.00,NULL,101,70,'2016-03-03 00:00:00'),(205,'Shelley','Higgins','SHIGGINS','515.123.8080','AC_MGR',12000.00,NULL,101,110,'2016-03-03 00:00:00'),(206,'William','Gietz','WGIETZ','515.123.8181','AC_ACCOUNT',8300.00,NULL,205,110,'2016-03-03 00:00:00');
/*Table structure for table `jobs` */
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `jobs`;
CREATE TABLE `jobs` (
`job_id` varchar(10) NOT NULL,
`job_title` varchar(35) DEFAULT NULL,
`min_salary` int(6) DEFAULT NULL,
`max_salary` int(6) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`job_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=gb2312;
/*Data for the table `jobs` */
insert into `jobs`(`job_id`,`job_title`,`min_salary`,`max_salary`) values ('AC_ACCOUNT','Public Accountant',4200,9000),('AC_MGR','Accounting Manager',8200,16000),('AD_ASST','Administration Assistant',3000,6000),('AD_PRES','President',20000,40000),('AD_VP','Administration Vice President',15000,30000),('FI_ACCOUNT','Accountant',4200,9000),('FI_MGR','Finance Manager',8200,16000),('HR_REP','Human Resources Representative',4000,9000),('IT_PROG','Programmer',4000,10000),('MK_MAN','Marketing Manager',9000,15000),('MK_REP','Marketing Representative',4000,9000),('PR_REP','Public Relations Representative',4500,10500),('PU_CLERK','Purchasing Clerk',2500,5500),('PU_MAN','Purchasing Manager',8000,15000),('SA_MAN','Sales Manager',10000,20000),('SA_REP','Sales Representative',6000,12000),('SH_CLERK','Shipping Clerk',2500,5500),('ST_CLERK','Stock Clerk',2000,5000),('ST_MAN','Stock Manager',5500,8500);
/*Table structure for table `locations` */
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `locations`;
CREATE TABLE `locations` (
`location_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`street_address` varchar(40) DEFAULT NULL,
`postal_code` varchar(12) DEFAULT NULL,
`city` varchar(30) DEFAULT NULL,
`state_province` varchar(25) DEFAULT NULL,
`country_id` varchar(2) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`location_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=3201 DEFAULT CHARSET=gb2312;
/*Data for the table `locations` */
insert into `locations`(`location_id`,`street_address`,`postal_code`,`city`,`state_province`,`country_id`) values (1000,'1297 Via Cola di Rie','00989','Roma',NULL,'IT'),(1100,'93091 Calle della Testa','10934','Venice',NULL,'IT'),(1200,'2017 Shinjuku-ku','1689','Tokyo','Tokyo Prefecture','JP'),(1300,'9450 Kamiya-cho','6823','Hiroshima',NULL,'JP'),(1400,'2014 Jabberwocky Rd','26192','Southlake','Texas','US'),(1500,'2011 Interiors Blvd','99236','South San Francisco','California','US'),(1600,'2007 Zagora St','50090','South Brunswick','New Jersey','US'),(1700,'2004 Charade Rd','98199','Seattle','Washington','US'),(1800,'147 Spadina Ave','M5V 2L7','Toronto','Ontario','CA'),(1900,'6092 Boxwood St','YSW 9T2','Whitehorse','Yukon','CA'),(2000,'40-5-12 Laogianggen','190518','Beijing',NULL,'CN'),(2100,'1298 Vileparle (E)','490231','Bombay','Maharashtra','IN'),(2200,'12-98 Victoria Street','2901','Sydney','New South Wales','AU'),(2300,'198 Clementi North','540198','Singapore',NULL,'SG'),(2400,'8204 Arthur St',NULL,'London',NULL,'UK'),(2500,'Magdalen Centre, The Oxford Science Park','OX9 9ZB','Oxford','Oxford','UK'),(2600,'9702 Chester Road','09629850293','Stretford','Manchester','UK'),(2700,'Schwanthalerstr. 7031','80925','Munich','Bavaria','DE'),(2800,'Rua Frei Caneca 1360 ','01307-002','Sao Paulo','Sao Paulo','BR'),(2900,'20 Rue des Corps-Saints','1730','Geneva','Geneve','CH'),(3000,'Murtenstrasse 921','3095','Bern','BE','CH'),(3100,'Pieter Breughelstraat 837','3029SK','Utrecht','Utrecht','NL'),(3200,'Mariano Escobedo 9991','11932','Mexico City','Distrito Federal,','MX');
/*!40101 SET SQL_MODE=@OLD_SQL_MODE */;
/*!40014 SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=@OLD_FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS */;
/*!40014 SET UNIQUE_CHECKS=@OLD_UNIQUE_CHECKS */;
/*!40111 SET SQL_NOTES=@OLD_SQL_NOTES */;
基础查询
语法:
select 查询列表
from 表名
特点:
- 查询列表可以是:表中的字段、常量值、表达式、函数
- 查询的结果是一个虚拟的表格
测试:
# 1. 查询表中的字段
select last_name
from employees;
# 2. 查询表中的多个字段
select last_name, salary, email
from employees;
# 3. 查询表中的所有字段
select employee_id,
first_name,
last_name,
email,
phone_number,
job_id,
salary,
commission_pct,
manager_id,
department_id,
hiredate
from employees;
select *
from employees;
# 4. 查询常量值
select 100;
select 'john';
# 5. 查询表达式
select 100 % 98;
# 6. 查询函数
select VERSION();
# 7. 起别名
# 方式1 使用as
select 100 % 98 AS 结果;
select last_name AS 姓, first_name AS 名
from employees;
# 方式2 使用空格
select last_name 姓, first_name 名
from employees;
# 案例:查询salary,显示结果为out put
select salary as "out put"
from employees;
# 8. 去重
# 案例:查询员工表中涉及到的所有部门编号
select distinct department_id
from employees;
# 9. 加号(+)的作用
/*
java中的+号:
①:运算符,两个操作数都为数值型
②:连接符,只要有一个操作数为字符串
mysql中的+号
仅仅有一个功能,就是运算符
select 100+90; 两个操作数为数值型,则做加法运算
select '123'+90; 其中一方为字符型,试图将字符型数值转换成数值型,如果转换成功,则继续做加法运算
select 'john'+90; 如果转换失败,则将字符型转换为0
select null+10; 只要其中一方为null,则结果肯定为null
*/
# 案例:查询员工名和姓连接成一个字段,并显示为姓名
select CONCAT('a', 'b', 'c') AS 结果;
select concat(last_name, first_name) as 姓名
from employees;
条件查询
语法:
select 查询列表
from 表名
where 筛选条件;
分类:
-
按条件表达式筛选
条件运算符:> < = != <> >= <=
-
按逻辑表达式筛选
逻辑运算符:&& || ! and or not
作用:用于连接条件表达式
-
模糊查询
like
between and
in
is null
-
安全等于:<=>可以判断null值也可以判断普通数值
测试:
# 条件查询
# 一、按条件表达式筛选
# 案例1:查询工资>12000的员工信息
select *
from employees
where salary > 12000;
# 案例2:查询部门编号不等于90号的员工名和部门编号 可以用<>或者!=
select last_name, department_id
from employees
where department_id <> 90;
# 二、按逻辑表达式筛选
# 案例1:查询工资在10000到20000之间的员工名、工资及奖金
select last_name, salary, commission_pct
from employees
where salary >= 10000
and salary <= 20000;
# 案例2:查询部门编号不是在90到110之间,或者工资高于15000的员工信息
select *
from employees
where department_id < 90
OR department_id > 110
OR salary > 15000;
select *
from employees
where NOT (department_id >= 90 AND department_id <= 110)
OR salary > 15000;
# 三、模糊查询
/*
like:
通配符:
%:任意多个字符
_:任意单个字符
*/
# 案例1:查询员工名中包含字符a的员工信息
select *
from employees
where last_name like '%a%';
# 案例2:查询员工名中第三个字符为n,第五个字符为l的员工名和工资
select last_name, salary
from employees
where last_name like '__n_l%';
# 案例3:查询员工名中第二个字符为_的员工名(转义字符)
# 方式1:默认\转义
select last_name
from employees
where last_name like '_\_%';
# 方式2:指定转义字符$
select last_name
from employees
where last_name like '_$_%' escape '$';
/*
between and
①:使用between and 可以提高语句的简洁度
②:包含临界值
③:两个临界值不要调换顺序
*/
# 案例1:查询员工编号在100到120之间的员工信息
select *
from employees
where employee_id >= 100
AND employee_id <= 120;
select *
from employees
where employee_id between 100 AND 120;
/*
in
用于判断某字段的值是否属于in列表中的某一项
①:使用in提高语句简洁度
②:in列表的值类型必须统一或兼容
③:
*/
# 案例:查询员工的工种编号是 IT_PROG、AD_VP、AD_PRES中的一个的员工名和工种编号
select last_name, job_id
from employees
where job_id in ('IT_PROG', 'AD_VP', 'AD_PRES');
/*
is null / is not null
= 或者 <> 不能用于判断null值
*/
# 案例1:查询没有奖金的员工名和奖金率
select last_name, commission_pct
from employees
where commission_pct is NULL;
/*
安全等于 <=> 可以判断null值
*/
# 案例1:查询没有奖金的员工名和奖金率
select last_name, commission_pct
from employees
where commission_pct <=> null;
# 案例2:查询工资为12000的员工信息
select last_name, salary
from employees
where salary <=> 12000;
# 综合案例:
# 1. 查询工资大于12000的员工姓名和工资
select last_name, salary
from employees emp
where emp.salary > 12000;
# 2. 查询员工号为176的员工的姓名和部门号以及年薪
select last_name, department_id, salary * 12 * (1 + IFNULL(commission_pct, 0)) 年薪
from employees emp
where emp.employee_id = 176;
# 3. 选择工资不在5000到12000的员工的姓名和工资
select emp.last_name, emp.salary
from employees emp
where emp.salary not between 5000 and 12000;
# 4. 选择在20或50号部门工作的员工姓名和部门号
select emp.last_name, emp.department_id
from employees emp
where emp.employee_id between 20 and 50;
# 5. 选择公司中没有管理者的员工姓名及job_id
select emp.last_name, emp.job_id
from employees emp
where emp.manager_id is null;
# 6. 选择公司中有奖金的员工姓名、工资和奖金级别
select emp.last_name, emp.salary, emp.commission_pct
from employees emp
where emp.commission_pct is not null;
# 7. 选择员工姓名的第三个字母是a的员工姓名
select emp.last_name
from employees emp
where emp.last_name like '__a%';
# 8. 选择姓名中有字母a和e的员工姓名
select emp.last_name
from employees emp
where emp.last_name like '%a%'
OR emp.last_name like '%e%';
# 9. 显示出表employee中first_name以'e'结尾的员工信息
select first_name, last_name
from employees
where first_name like '%e';
# 10. 显示出employee中部门编号在80-100之间的姓名和职位
select emp.last_name, emp.job_id
from employees emp
where emp.department_id between 80 and 100;
# 11. 显示出employee的manager_id是100,101,110的员工姓名、职位
select emp.last_name, emp.job_id
from employees emp
where emp.manager_id in (100, 101, 110);
测试题
# 一、查询没有奖金,工资小于18000的salary、last_name
select emp.salary, emp.last_name
from employees emp
where emp.commission_pct is null
AND emp.salary < 1800;
# 二、 查询employees表中,job_id不为“IT”或者工资为12000的员工信息
select emp.last_name,emp.job_id,emp.salary
from employees emp
where emp.job_id != 'IT' OR emp.salary = 12000;
# 三、 查看部门departments表的结构
desc departments;
# 四、查询部门departments表中涉及到了哪些位置编号
select distinct location_id
from departments;
/*
五、 经典面试题:
试问: select * from employees
和 select * from employees where commission_pct like '%%" and last_name like '%%';
结果是否一样?说明原因
*/
select *
from employees;
select *
from employees where commission_pct like '%%' and last_name like '%%';
# 答案是不一样,如果判断的值里有null值,则会不一样,如果都是or关键字就一样;
排序查询
语法:
select 查询列表
from 表
【where 筛选条件】
order by 排序列表 asc(升序默认)|desc(降序)
支持按表达式排序、按别名排序、按函数排序、多个字段排序
测试:
# 排序查询
use myemployees;
# 案例1:查询员工信息,要求工资从高到低排序
select *
from employees emp
order by emp.salary desc;
# 案例2:查询部门编号>=90的员工信息,按入职时间的先后进行排序【添加了筛选条件】
select *
from employees emp
where emp.department_id >= 90
order by hiredate asc;
# 案例3:按年薪的高低显示员工的信息和年薪【按表达式排序】
select emp.*, emp.salary * 12 * (1 + ifnull(emp.commission_pct, 0)) year_salary
from employees emp
order by emp.salary * 12 * (1 + ifnull(emp.commission_pct, 0)) desc;
# 案例4:按年薪的高低显示员工的信息和年薪【按别名排序】
select emp.*, emp.salary * 12 * (1 + ifnull(emp.commission_pct, 0)) year_salary
from employees emp
order by year_salary desc;
# 案例5:按姓名的长度显示员工的姓名和工资【按函数排序】
select length(last_name) 字节长度, last_name, salary
from employees
order by 字节长度 desc;
# 案例6:查询员工信息,要求先按工资排序[升序],再按员工编号排序[降序]【按多个字段排序】
select *
from employees
order by salary, employee_id desc;
测试题
# 测试
# 1. 查询员工的姓名和部门号以及年薪,按年薪降序、姓名升序
select last_name, department_id, salary * 12 * (1 + ifnull(commission_pct, 0)) 年薪
from employees
order by 年薪 desc, last_name asc;
# 2. 选择工资不再8000到17000的员工的姓名和工资,按工资降序
select last_name, salary
from employees e
where e.salary not between 8000 and 17000
order by salary desc;
# 3. 查询邮箱中包含e的员工信息,并先按邮箱的字节数降序,再按部门号升序
select *
from employees e
where e.email like '%e%'
order by length(e.email) desc, e.department_id;
常见函数
概念:类似于java中的方法,将一组逻辑语句封装在方法体中,对外暴露方法名
好处:
- 隐藏了实现细节
- 提高代码的重用性
**调用:**select 函数名(实参列表)【from表】;
特点:
- 叫什么(函数名)
- 干什么(函数功能)
分类:
-
单行函数
concat、length、ifnull等
-
分组函数
主要用于统计使用,又称为统计函数、聚合函数、组函数
字符函数
length
# 1. length():获取参数值的字节个数,utf-8一个中文3个字节
select length('john');
select length('张三丰hahaha');
show variables like '%char%';
concat
# 2. concat 拼接字符串
select concat(last_name, '_', first_name) 姓名
from employees;
upper、lower
# 3. upper、lower 大小写转换
select upper('john');
select lower('JoHn');
select concat(upper(last_name), lower(first_name)) 姓名
from employees;
substr、substring
# 4. substr、substring 截取字符 4个重载,字符长度
select substr('李莫愁爱上了陆展元', 7) out_put;
select substr('李莫愁爱上了陆展元', 1, 3) out_put;
# 案例:姓名中首字符大写,其他字符小写,然后用下划线_拼接显示出来
select last_name, concat(upper(substr(last_name, 1, 1)), '_', lower(substr(last_name, 2))) 结果
from employees;
instr
# 5. instr:返回子串第一次出现的位置,如果找不到就返回0
select instr('杨不悔爱上了殷六侠', '殷六侠');
trim
# 6. trim:去前后空格
select length(trim(' 张翠山 ')), trim(' 张翠山 ') as out_put;
select trim('a' from 'aaaaaaaaaaaa张aaaaaaa翠山aaaaa') as out_put;
lpad、rpad
# 7. lpad:用指定的字符实现左填充指定长度,超过则截断
select lpad('殷素素',10,'*') as out_put;
# 8. rpad:用指定的字符实现左填充指定长度,超过则截断
select rpad('殷素素',12,'ab') as out_put;
replace
# 9. replace 所有都会替换
select replace('周芷若-张无忌爱上了周芷若','周芷若','赵敏') as out_put;
数学函数
round
# 1. round 四舍五入
select round(-1.65);
select round(1.567,2);
ceil
# 2. ceil 向上取整,返回>=该参数的最小整数
select ceil(1.002); # 2
select ceil(-1.002);# -1
floor
# 3. floor 向下取整,返回<=该参数的最大整数
select floor(9.99); #9
select floor(-9.99);# 10
truncate
# 4. truncate 截断 保留几位小数,直接截断
select truncate(1.65,1);
mod
# 5. mod取余 a%b a-a/b*b
select MOD(10,3);# 1
select mod (-10,3);# -1
日期函数
| 序号 | 格式符 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | %Y | 四位的年份 |
| 2 | %y | 两位的年份 |
| 3 | %m | 月份(01,02,03......11,12) |
| 4 | %c | 月份(1,2,3......11,12) |
| 5 | %d | 日(01,02,03......) |
| 6 | %H | 小时(24小时制) |
| 7 | %h | 小时(12小时制) |
| 8 | %i | 分钟(00,01......59) |
| 9 | %s | 秒(00,01......59) |
now
# 1. now 返回当前系统日期+时间
select now();
curdate/current_date
# 2. curdate/current_date 返回当前系统日期,不包含时间
select curdate();
select current_date();
curtime/current_time
# 3. curtime/current_time 返回当前系统时间,不包含日期
select curtime();
select current_time();
year/month/day/hour/minute/second
# 4. year/month/day/hour/minute/second获取指定部分——年月日、时分秒
select year(now()) 年;
select month('1998-1-1') 年;
select year(hiredate) from employees;
select month(hiredate) from employees;
select MONTHNAME(hiredate) from employees;
str_to_date
# 5. str_to_date:将日期格式的字符转换成指定格式的日期
select str_to_date('1998-3-2 1','%Y-%c-%d %h');
# 案例:查询入职日期为1992-4-3的员工信息
select * from employees where hiredate='1992-4-3';
select * from employees where hiredate=str_to_date('4-3 1992','%c-%d %Y');
date_format
# 6. date_format:将日期转换成字符
select date_format(now(),'%Y年%m月%d日');
# 案例:查询有奖金的员工名和入职日期(xx月/xx日 xx年)
select last_name,DATE_FORMAT(hiredate,'%m月/%d日 %y年')
from employees where commission_pct is not null;
其他函数【补充】
version
# 1. 查看当前数据库版本
select version();
database
# 2. 查看当前所在数据库
select database();
user
# 3. 当面用户
select user();
流程控制函数【补充】
if
# 1. if函数:类似三目运算符 表达式1结果为true则返回表达式2的值,false则返回表达式3的值
select if(10<5,'真','假');
# 案例:有奖金则返回有,否则返回无
select last_name,commission_pct,if(commission_pct is null,'无奖金','有奖金')
from employees;
case
语法一:
case 要判断的字段或表达式
when 常量1 then 要显示的值1或语句1;
when 常量2 then 要显示的值2或语句2;
...
else 要显示的值n或语句n;
end
# 2. case函数的使用一:switch case的效果
/*
案例:查询员工的工资,要求
部门号=30,显示的工资为1.1倍
部门号=40,显示的工资为1.2倍
部门号=50,显示的工资为1.3倍
其他部门,显示的工资为原工资
*/
select salary,
department_id,
case department_id when 30 then salary * 1.1 when 40 then salary * 1.2 when 50 then salary * 1.3 else salary end
from employees;
语法二:
case
when 条件1 then 要显示的值1或语句1;
when 条件2 then 要显示的值2或语句2;
...
else 要显示的值n或语句n;
end
# 3. case函数的使用二:类似于 if-else if-else
/*
案例:查询员工的工资情况
如果工资>20000,显示A级别
如果工资>15000,显示B级别
如果工资>10000,显示C级别
否则,显示D级别
*/
select salary,
case when salary > 20000 then 'A' when salary > 15000 then 'B' when salary > 10000 then 'C' else 'D' end
from employees;
综合测试
# 综合测试
# 1. 显示系统时间(注:日期+时间)
select now();
# 2. 查询员工号、姓名、工资、工资提高百分之20%之后的结果
select employee_id, last_name, salary, salary * 1.2
from employees;
# 3. 将员工的姓名按首字母排序,并写出姓名的长度
select substr(last_name, 1, 1) 首字符, last_name, length(last_name)
from employees
order by 首字符;
/*
4. 做一个查询,产生下面的结果:
<last_name>earns<salary>monthly but wants<salary*3>
*/
select CONCAT(last_name, ' earns ', salary, ' monthly but wants ', salary * 3)
from employees;
/*
5. 使用case-when,按照下面条件
job_id grade
AD_PRES A
ST_MAN B
IT_PROG C
SA_REP D
ST_CLERK E
*/
select last_name,
job_id,
case
when job_id = 'AD_PRES' then 'A'
when job_id = 'ST_MAN' then 'B'
when job_id = 'IT_PROG' then 'C'
when job_id = 'SA_REP' then 'D'
when job_id = 'ST_CLERK' then 'E'
end AS grade
from employees;
分组函数
**功能:**用于统计使用,又称为聚合函数、统计函数、组函数
分类:
- sum:求和
- avg:平均值
- max:最大值
- min:最小值
- count:计算个数
特点:
- sum、avg一般用于处理数值型
- max、min、count可以处理任何类型
- 以上函数都会自动忽略null值
- 可以和distinct搭配使用
- count函数单独介绍
- count(字段):可以统计单个字段行数(非null才会统计)
- count(*):统计行数,只要有一行的一个字段不为空就会被统计,所以就是所有记录数
- count(1):相当于临时加上一列,所有的值都为1,也用于统计行数;
- 效率:
- MYISAM存储引擎下:count(*)效率最高
- INNODB存储引擎下:count(*)和count(1)效率差不多,但是比count(字段)高一些;
- 和分组函数一同查询的字段有限制,一般要求是group by之后的字段
sum/avg/max/min/count使用
# 分组函数
use myemployees;
# 1. 简单使用
select sum(salary)
from employees;
select avg(salary)
from employees;
select min(salary)
from employees;
select max(salary)
from employees;
select count(*)
from employees e;
select sum(salary), avg(salary), max(salary), min(salary), count(salary)
from employees;
select sum(salary), round(avg(salary), 2), max(salary), min(salary), count(salary)
from employees;
# 2. 参数支持哪些类型
select sum(last_name), avg(last_name)
from employees;
select sum(hiredate), avg(hiredate)
from employees;
select max(last_name), min(last_name)
from employees;
select max(hiredate), min(hiredate)
from employees;
select count(commission_pct)
from employees;
select count(last_name)
from employees;
# 3. 是否忽略null值
select sum(commission_pct), avg(commission_pct), sum(commission_pct) / 35, sum(commission_pct) / 107
from employees;
select max(commission_pct), min(commission_pct)
from employees;
select count(commission_pct)
from employees;
# 4. 和distinct搭配使用
select sum(distinct salary), sum(salary)
from employees;
select count(distinct salary), count(salary)
from employees;
综合测试
# 综合测试
# 1. 查询公司员工工资的最大值、最小值、平均值、总和
select max(salary), min(salary), avg(salary), sum(salary)
from employees;
# 2. 查询员工表中的最大入职时间和最小入职时间的相差天数(DATEDIFF)
select max(hiredate),min(hiredate),DATEDIFF(max(hiredate),min(hiredate))
from employees;
# 3. 查询部门编号为90的员工个数
select count(*)
from employees
where department_id=90;
分组查询
比如查询每个部门的平均工资等操作,需要对部门进行分组;
语法:
select column,group_function(column)
from table
[where condition]
[group by group_by_expression]
[having condition]
[order by column]
明确:WHERE条件一定要放在FROM后面;
注意:
查询列表比较特殊,要求是分组函数或者group by后面出现的字段
特点:
- 分组查询中的筛选条件分为两类(数据源不同)
- 分组前筛选(原始表)where,在from后面,group by前面
- 分组后筛选(分组后的结果集)having,在group by后面
- 分组函数做条件肯定是放在having子句中;
- 能用分组前筛选的,优先考虑使用分组前筛选,性能更好
- group by 子句支持单个字段分组、多个字段分组(多个字段之间用逗号隔开,没有顺序要求),表达式跟函数也支持(用的比较少);
- 也可以添加排序,放在整个分组查询的最后;
简单的分组查询
# 案例1:查询每个工种的最高工资
select max(salary), job_id
from employees
group by job_id;
# 案例2:查询每个位置上的部门个数
select count(*), location_id
from departments
group by location_id;
添加分组前的筛选条件
# 案例1:查询邮箱中包含a字符的,每个部门的平均工资
select department_id, avg(salary)
from employees
where email like '%a'
group by department_id;
# 案例2:查询有奖金的每个领导手下员工的最高工资
select max(salary), manager_id
from employees
where commission_pct is not null
group by manager_id;
添加分组后的筛选条件
# 案例1:查询哪个部门的员工个数>2
# ①:查询每个部门的员工个数
select department_id, count(*)
from employees
group by department_id;
# ②:根据①得到的结果进行筛选,查询哪些部门的员工个数>2
select department_id, count(*)
from employees
group by department_id
having count(*) > 2;
# 案例2:查询每个工种有奖金的员工,且最高工资>12000的工种编号和最高工资
select job_id, max(salary)
from employees
where commission_pct is not null
group by job_id
having max(salary) > 12000;
# 案例3:领导编号>102的每个领导手下的最低工资>5000的领导编号是哪个,以及其最低工资
select manager_id, min(salary)
from employees
where manager_id > 102
group by manager_id
having min(salary) > 5000;
按表达式或函数分组
# 案例:按员工姓名的长度分组,查询每一组的员工个数,筛选员工个数>5的有哪些
select length(last_name), count(*)
from employees
group by length(last_name)
having count(*) > 5;
按多个字段分组
# 案例:查询每个部门每个工种的员工的平均工资
select department_id, job_id, avg(salary)
from employees
group by department_id, job_id;
添加排序
## 案例:查询每个部门每个工种的员工的平均工资,部门不为null且平均工资高于10000,并且按平均工资的降序排序
select department_id, job_id, avg(salary)
from employees
where department_id is not null
group by department_id, job_id
having avg(salary) > 10000
order by avg(salary) desc;
综合测试
# 综合测试
# 1. 查询各个job_id的员工工资的最大值、最小值、平均值、总和,并按job_id排序
select job_id, max(salary), min(salary), avg(salary), sum(salary)
from employees
group by job_id
order by job_id;
# 2. 查询员工最高工资和最低工资的差距
select max(salary) - min(salary)
from employees;
# 3. 查询各个管理者手下员工的最低工资,其中最低工资不能低于6000,没有管理者的员工不计算在内
select manager_id, min(salary)
from employees
where manager_id is not null
group by manager_id
having min(salary) >= 6000;
# 4. 查询所有部门的编号,员工数量和工资平均值,并按平均工资降序排序
select department_id, count(*), avg(salary)
from employees
group by department_id;
# 5. 选择各个job_id的员工人数
select count(*),job_id
from employees
group by job_id;
连接查询
多表连接,当查询的字段来自多个表自然就要用到连接查询;
先导入表:
/*
SQLyog Ultimate v10.00 Beta1
MySQL - 5.7.18-log : Database - girls
*********************************************************************
*/
/*!40101 SET NAMES utf8 */;
/*!40101 SET SQL_MODE=''*/;
/*!40014 SET @OLD_UNIQUE_CHECKS=@@UNIQUE_CHECKS, UNIQUE_CHECKS=0 */;
/*!40014 SET @OLD_FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=@@FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS, FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=0 */;
/*!40101 SET @OLD_SQL_MODE=@@SQL_MODE, SQL_MODE='NO_AUTO_VALUE_ON_ZERO' */;
/*!40111 SET @OLD_SQL_NOTES=@@SQL_NOTES, SQL_NOTES=0 */;
CREATE DATABASE /*!32312 IF NOT EXISTS*/`girls` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */;
USE `girls`;
/*Table structure for table `admin` */
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `admin`;
CREATE TABLE `admin` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`username` varchar(10) NOT NULL,
`password` varchar(10) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=3 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
/*Data for the table `admin` */
insert into `admin`(`id`,`username`,`password`) values (1,'john','8888'),(2,'lyt','6666');
/*Table structure for table `beauty` */
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `beauty`;
CREATE TABLE `beauty` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`sex` char(1) DEFAULT '女',
`borndate` datetime DEFAULT '1987-01-01 00:00:00',
`phone` varchar(11) NOT NULL,
`photo` blob,
`boyfriend_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=13 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
/*Data for the table `beauty` */
insert into `beauty`(`id`,`name`,`sex`,`borndate`,`phone`,`photo`,`boyfriend_id`) values (1,'柳岩','女','1988-02-03 00:00:00','18209876577',NULL,8),(2,'苍老师','女','1987-12-30 00:00:00','18219876577',NULL,9),(3,'Angelababy','女','1989-02-03 00:00:00','18209876567',NULL,3),(4,'热巴','女','1993-02-03 00:00:00','18209876579',NULL,2),(5,'周冬雨','女','1992-02-03 00:00:00','18209179577',NULL,9),(6,'周芷若','女','1988-02-03 00:00:00','18209876577',NULL,1),(7,'岳灵珊','女','1987-12-30 00:00:00','18219876577',NULL,9),(8,'小昭','女','1989-02-03 00:00:00','18209876567',NULL,1),(9,'双儿','女','1993-02-03 00:00:00','18209876579',NULL,9),(10,'王语嫣','女','1992-02-03 00:00:00','18209179577',NULL,4),(11,'夏雪','女','1993-02-03 00:00:00','18209876579',NULL,9),(12,'赵敏','女','1992-02-03 00:00:00','18209179577',NULL,1);
/*Table structure for table `boys` */
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `boys`;
CREATE TABLE `boys` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`boyName` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`userCP` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=5 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
/*Data for the table `boys` */
insert into `boys`(`id`,`boyName`,`userCP`) values (1,'张无忌',100),(2,'鹿晗',800),(3,'黄晓明',50),(4,'段誉',300);
/*!40101 SET SQL_MODE=@OLD_SQL_MODE */;
/*!40014 SET FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS=@OLD_FOREIGN_KEY_CHECKS */;
/*!40014 SET UNIQUE_CHECKS=@OLD_UNIQUE_CHECKS */;
/*!40111 SET SQL_NOTES=@OLD_SQL_NOTES */;
分类:
- 按年代分类:
- sql92标准:mysql中仅支持内连接
- sql99标准【推荐】:mysql中支持内连接+外连接(左外和右外【Oracle支持全外连接】)+交叉连接
- 按功能分类:
- 内连接
- 等值连接
- 非等值连接
- 自连接
- 外连接
- 左外连接
- 右外连接
- 全外连接
- 交叉连接
- 内连接
sql92标准
注意:92语法只支持内连接,所以在连接条件为null的时候,可能会得不到想要的结果
- 多表等值连接的结果为多表的交集部分
- n表连接,至少需要n-1个连接条件
- 多表的顺序没有要求
- 一般需要为表起别名
- 可以搭配前面介绍的所有子句使用,如排序、分组、筛选
等值连接
# 1. 等值连接
# 案例1:查询女神名和对应的男神名
select beauty.name, boys.boyName
from boys,
beauty
where boys.id = beauty.boyfriend_id;
# 案例2:查询员工名和对应的部门名
select e.last_name, d.department_name
from employees e,
departments d
where e.department_id = d.department_id;
# 案例3:查询员工名、工种编号、工种名
select e.last_name, e.job_id, j.job_title
from employees e,
jobs j
where e.job_id = j.job_id;
# 案例4:查询有奖金的员工名、部门名【加筛选条件】
select e.last_name, d.department_name
from employees e,
departments d
where e.department_id = d.department_id
and e.commission_pct is not null;
# 案例5:查询城市中第二个字符为o的部门名和城市名【加筛选条件】
select d.department_name, l.city
from locations l,
departments d
where d.location_id = l.location_id
and l.city like '_o%';
# 案例6:查询每个城市的部门个数【加分组】
select city, count(*)
from locations l,
departments d
where l.location_id = d.location_id
group by l.city;
# 案例7:查询有奖金的每个部门的部门名以及部门的领导编号,以及该部门的最低工资【加分组】
select d.department_name, d.manager_id, min(e.salary)
from employees e,
departments d
where e.department_id = d.department_id
and e.commission_pct is not null
group by d.department_name, d.manager_id;
# 案例8:查询每个工种的工种名和员工的个数,并且按员工的个数降序【加排序】
select j.job_title, count(*)
from jobs j,
employees e
where e.job_id = j.job_id
group by j.job_title
order by count(*) desc;
# 案例9:查询员工名,部门名,所在城市【三表查询】
select e.last_name, d.department_name, l.city
from employees e,
departments d,
locations l
where e.department_id = d.department_id
and d.location_id = l.location_id;
非等值连接
先建立一张工资等级表
create table job_grades
(
grade_level varchar(3),
lowest_sal int,
highest_sal int
);
insert into job_grades
values ('A', 1000, 2999),
('B', 3000, 5999),
('C', 6000, 9999),
('D', 10000, 14999),
('E', 15000, 24999),
('F', 25000, 40000);
# 2. 非等值连接
# 案例1:查询员工的工资和工资级别
select e.last_name, e.salary, j.grade_level
from employees e,
job_grades j
where e.salary between j.lowest_sal and j.highest_sal;
自连接
# 3. 自连接
# 案例:查询员工名以及其上级的名字
select e.last_name, m.last_name
from employees e,
employees m
where e.manager_id = m.employee_id;
综合测试
# 综合测试 1
# 1. 显示员工表中的最大工资、工资平均值
select max(salary), avg(salary)
from employees;
# 2. 查询员工表的employee_id,job_id,last_name,按department_id降序,salary升序
select employee_id, job_id, last_name
from employees
order by department_id desc, salary asc;
# 3. 查询员工表的job_id包含a和e的,并且a在e前面
select job_id
from employees
where job_id like '%a%e%';
/*
4. 已知表student,有id(学号),name,gradeId(年级编号)
表grade,有id(年级编号),name(年级名)
表result,有id,score,studentNo(学号)
要求查询姓名、年级名、成绩
select s.name,g.name,r.score
from student s,
grade g,
result r
where s.gradeId = g.id and s.id = r.studentNo;
*/
# 5. 显示当前日期,以及去前后空格,截取子字符串的函数
select now(), trim(' 123 '), substr('123456', 3);
# 综合测试 2
# 1. 显示所有员工的姓名,部门号和部门名称
select e.last_name, e.department_id, d.department_name
from employees e,
departments d
where e.department_id = d.department_id;
# 2. 查询90号部门员工的job_id和90号部门location_id
select e.job_id, d.location_id
from employees e,
departments d
where e.department_id = d.department_id
and e.department_id = 90;
# 3. 选择所有有奖金的员工的 last_name,department_name,location_id,city
select e.last_name, d.department_name, d.location_id, l.city
from employees e,
departments d,
locations l
where e.department_id = d.department_id
and d.location_id = l.location_id
and e.commission_pct is not null;
# 4. 选择city在Toronto工作的员工的last_name,job_id,department_id,department_name
select e.last_name, e.job_id, d.department_id, d.department_name
from employees e,
departments d,
locations l
where e.department_id = d.department_id
and d.location_id = l.location_id
and l.city = 'Toronto';
# 5. 查询每个工种、每个部门的部门名、工种名和最低工资
select d.department_name, j.job_title, min(e.salary)
from employees e,
departments d,
jobs j
where e.department_id = d.department_id
and e.job_id = j.job_id
group by j.job_id, d.department_name;
# 6. 查询每个国家下的部门个数大于2的国家编号
select l.country_id, count(*)
from locations l,
departments d
where d.location_id = l.location_id
group by l.country_id
having count(*) > 2;
# 7. 选择指定员工的姓名、员工号、管理者的姓名和员工号
select e.last_name, e.employee_id, m.last_name, m.employee_id
from employees e,
employees m
where e.manager_id = m.employee_id;
sql99标准
语法:
select 查询列表
from 表1 别名
【连接类型】join 表2
on 连接条件
【where 筛选条件】
【group by 分组】
【having 筛选条件】
【order by 排序列表】
分类:
内连接:inner
外连接:
- 左外:left 【outer】
- 右外:right 【outer】
- 全外:MySQL不支持,Oracle支持,full【outer】
交叉连接:cross
内连接
特点:
- 添加排序、分组、筛选
- inner可以省略
- 筛选条件可以放在where后面,连接条件放在on后面,提高分离性,便于阅读
- inner join连接和sql92语法中的等值连接效果是一样的,都是查询交集;
等值连接
# 二、sql99标准
# 1. 内连接
# 【内连接】 等值连接
# 案例1:查询员工名、部门名
select *
from employees e
inner join departments d on e.department_id = d.department_id;
# 案例2:查询名字中包含e的员工名和工种名(筛选)
select e.last_name, j.job_title
from employees e
inner join jobs j on e.job_id = j.job_id
where e.last_name like '%e%';
# 案例3:查询部门个数>3的城市名和部门个数(分组+筛选)
select l.city, count(*)
from departments d
inner join locations l on d.location_id = l.location_id
group by l.city
having count(*) > 3;
# 案例4:查询哪个部门的部门员工个数>3的部门名和员工个数,并按个数降序(排序)
select d.department_name, count(*)
from employees e
inner join departments d on e.department_id = d.department_id
group by e.department_id
having count(*) > 3
order by count(*) desc;
# 案例5:查询员工名、部门名、工种名,并按部门名降序
select e.last_name, d.department_name, j.job_title
from employees e
inner join departments d on e.department_id = d.department_id
inner join jobs j on e.job_id = j.job_id
order by d.department_name desc;
非等值连接
# 【内连接】非等值连接
# 案例1:查询员工的工资级别
select e.last_name, e.salary, jg.grade_level
from employees e
inner join job_grades jg
on e.salary between jg.lowest_sal and jg.highest_sal;
# 案例2:查询每个工资级别的个数>20,并且按工资级别的降序
select count(*), jg.grade_level
from employees e
inner join job_grades jg
on e.salary between jg.lowest_sal and jg.highest_sal
group by jg.grade_level
having count(*) > 20
order by jg.grade_level desc;
自连接
# 【内连接】自连接
# 案例1:查询员工的姓名、上级的名字
select e.last_name, m.last_name
from employees e
inner join employees m on e.manager_id = m.employee_id;
# 案例2:查询姓名包含k的员工、上级的名字
select e.last_name, m.last_name
from employees e
inner join employees m on e.manager_id = m.employee_id
where e.last_name like '%k%';
外连接
**应用场景:**用于查询一个表中有,另一个表中没有的记录
特点:
-
外连接的查询结果为主表中的所有记录,
如果从表中有和它匹配的,则显示匹配的值;
如果从表中没有匹配的,则显示null;
外连接查询结果 = 内连接结果 + 主表中有而从表中没有的记录
-
左外连接:left join,左边的是主表
-
右外连接:right join,右边的是主表
-
左外和右外交换两个表的顺序,可以实现同样的效果
# 2. 外连接
# 引入:查询男朋友不在男神表的女神名
use girls;
# 左外连接实现
select g.name
from beauty g
left outer join boys b on g.boyfriend_id = b.id
where b.id is null;
# 右外连接实现
select g.name
from boys b
right outer join beauty g on b.id = g.boyfriend_id
where b.id is null;
use myemployees;
# 案例1:查询哪个部门没有员工
select d.department_name, e.employee_id
from departments d
left outer join employees e on d.department_id = e.department_id
where e.employee_id is null;
全外连接
内连接的结果+表1中有但表2中没有的+表2中有但表1中没有的
交叉连接
笛卡尔乘积
92语法与99语法的总结
**功能:**sql99支持的多
**可读性:**sql99实现连接条件和筛选条件的分离,可读性较高
Join连接总结
-
内连接【inner join】
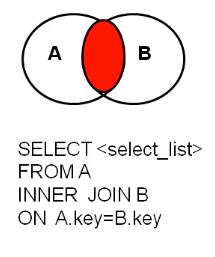
-
左外连接【left outer join】
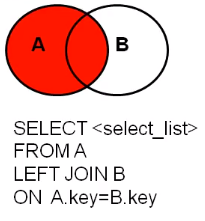
-
右外连接【right outer join】
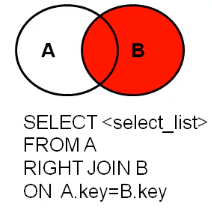
-
全外连接【full outer join】(MySQL不支持,Oracle支持)
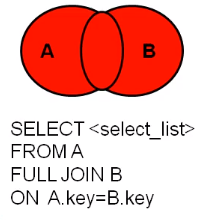
-
左外连接去除交集部分【left outer join+B.key为null】
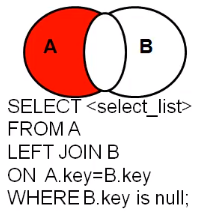
-
右外连接去除交集部分【right outer join+A.key为null】
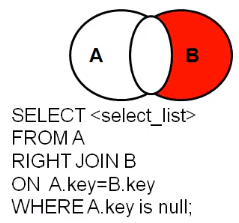
-
去除关联表交集部分
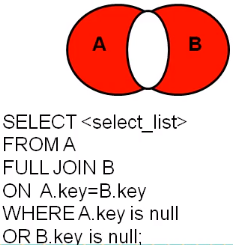
多表连接综合案例
# 综合案例
# 1. 查询编号>3的女神的男朋友信息,如果有则列出详细,如果没有则null填充
select g.*, b.*
from beauty g
left outer join boys b
on g.boyfriend_id = b.id
where g.id > 3;
# 2. 查询哪个城市没有部门
use myemployees;
select l.city
from departments d
left outer join locations l on l.location_id = d.location_id
where d.department_id is null;
# 3. 查询部门名为SAL或IT的员工信息
select e.last_name, d.department_id, d.department_name
from departments d
left join employees e on e.department_id = d.department_id
where d.department_name = 'SAL'
OR d.department_name = 'IT';
子查询
含义:
- 出现在其他语句中的select语句,称之为子查询或内查询;
- 外部的查询语句,称之为主查询或外查询
分类:
按子查询出现的位置
- select后面
- 仅仅标量子查询
- from后面
- 表子查询
- where或having后面
- 标量子查询(单行)
- 列子查询(多行)
- 行子查询(多列多行)
- exist后面(相关子查询)
- 表子查询
按结果集的行列数不同:
- 标量子查询(结果集只有一行一列)
- 列子查询(结果集只有一列多行)
- 行子查询(结果集只有一行多列)
- 表子查询(结果集一般为多行多列)
where或having后面
特点:
- 子查询放在小括号内
- 子查询一般放在条件的右侧
- 标量子查询,一般搭配着单行操作符使用(> < >= <= = <>)
- 列子查询,一般搭配多行操作符使用(in any some all)
- 子查询的执行优先于主查询查询,主查询的条件用到了子查询的结果
标量子查询(单行单列)
# 1. 标量子查询(单行子查询)
# 案例1:谁的工资比Abel高?
select e.last_name, e.salary
from employees e
where salary > (select e.salary
from employees e
where e.last_name = 'Abel');
# 案例2:返回job_id与141号员工相同,salary比143号员工多的员工姓名,job_id和工资
select e.last_name, e.job_id, e.salary
from employees e
where e.job_id = (select e.job_id from employees e where e.employee_id = 141)
and e.salary > (select e.salary from employees e where e.employee_id = 143);
# 案例3:返回公司工资最少的员工的last_name,job_id和salary
select e.last_name, e.job_id, e.salary
from employees e
where e.salary = (select min(e.salary)
from employees e);
# 案例4:查询最低工资>50号部门最低工资的部门id和其最低工资
select e.department_id, min(salary)
from employees e
group by e.department_id
having min(e.salary) > (select min(salary)
from employees
where department_id = 50);
列子查询(多行单列)
- 返回多行
- 使用多行比较操作符
| 操作符 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| IN / NOT IN | 等于列表中的任意一个,若不在列表中的任意一个 |
| ANY / SOME | 和子查询返回的某一个值比较 |
| ALL | 和子查询返回的所有值比较 |
# 2. 列子查询(多行)
# 案例1:返回location_id是1400或1700的部门中所有员工的姓名
select e.last_name
from employees e
where e.department_id in (select d.department_id
from departments d
where d.location_id in (1400, 1700));
# 案例2:返回其他工种中比job_id为“IT_PROG”工种任一工资低的员工的员工号、姓名、job_id以及salary
select e.employee_id, e.last_name, e.job_id, e.salary
from employees e
where e.job_id != 'IT_PROG'
AND e.salary < any (select distinct salary
from employees e
where e.job_id = 'IT_PROG');
select e.employee_id, e.last_name, e.job_id, e.salary
from employees e
where e.job_id != 'IT_PROG'
AND e.salary < (select max(e.salary)
from employees e
where e.job_id = 'IT_PROG');
# 案例3:返回其他工种中比job_id为“IT_PROG"部门所有工资都低的员工的员工号、姓名、job_id以及salary
select e.employee_id, e.last_name, e.job_id, e.salary
from employees e
where e.job_id != 'IT_PROG'
AND e.salary < all (
select distinct e.salary
from employees e
where e.job_id = 'IT_PROG');
select e.employee_id, e.last_name, e.job_id, e.salary
from employees e
where e.job_id != 'IT_PROG'
AND e.salary < (
select min(e.salary)
from employees e
where e.job_id = 'IT_PROG');
行子查询(结果集一行多列或多行多列)
# 3. 行子查询(一行多列或多列多行)
# 案例1:查询员工编号最小并且工资最高的员工信息
select *
from employees
where employee_id = (select min(e.employee_id)
from employees e)
AND salary = (select max(salary)
from employees e);
select *
from employees e
where (e.employee_id, e.salary) = (select min(employee_id), max(salary) from employees e);
select后面
只支持标量子查询(一行一列)
# 二、select后面
# 案例1:查询每个部门的员工个数
select d.*,
(
select count(*)
from employees e
where e.department_id = d.department_id
)
from departments d;
# 案例2:查询员工号为102的部门名
select e.employee_id, (select d.department_name from departments d where e.department_id = d.department_id)
from employees e
where e.employee_id = '102';
from后面
# 三、from后面
# 案例1:查询每个部门的平均工资的工资等级
select e.*, jg.grade_level
from (select avg(e.salary) salary, department_id
from employees e
group by e.department_id) e
left join job_grades jg
on e.salary between jg.lowest_sal and jg.highest_sal;
exists后面(相关子查询)
语法:
exists (完整的查询语句)
**结果:**0或1
# 四、exists后面(相关子查询)
# 案例1:查询有员工名的部门名
# exists
select d.department_name
from departments d
where exists(select * from employees e where e.department_id = d.department_id)
# in
select d.department_name
from departments d
where d.department_id in (
select e.department_id
from employees e);
综合测试
# 综合测试
# 1. 查询和Zlotkey相同部门的员工姓名和工资
select e.last_name, e.salary
from employees e
where e.department_id = (select e.department_id from employees e where e.last_name = 'Zlotkey');
# 2. 查询工资比公司平均工资高的员工的员工号,姓名和工资
select e.employee_id, e.last_name, e.salary
from employees e
where e.salary > (select avg(salary)
from employees);
# 3. 查询各部门中工资比本部门平均工资高的员工的员工号、姓名和工资
select e.employee_id, e.last_name, e.salary, d.avg_salary, e.department_id
from employees e
left join (select e.department_id, avg(e.salary) avg_salary
from employees e
group by e.department_id) d
on e.department_id = d.department_id
where e.salary > d.avg_salary;
# 4. 查询和姓名中包含字母u的员工在相同部门的员工的员工号和姓名
select e.employee_id, e.last_name
from employees e
where e.department_id in (
select distinct e.department_id
from employees e
where e.last_name like '%u%')
and e.last_name not like '%u%';
# 5. 查询在部门的location_id为1700的部门工作的员工的员工号
select e.employee_id
from employees e
where e.department_id in (
select distinct d.department_id
from departments d
where d.location_id = 1700);
# 6. 查询管理者是K_ing的员工姓名和工资
select e.last_name, e.salary
from employees e
where e.manager_id in (select e.employee_id from employees e where e.last_name = 'K_ing');
# 7. 查询工资最高的员工的姓名,要求first_name和last_name显示为一列,列名为姓.名
select concat(e.first_name, '.', e.last_name)
from employees e
where e.salary = (select max(e.salary) max_salary from employees e);
子查询经典案例
- 查询工资最低的员工信息:last_name,salary
- 查询平均工资最低的部门信息
- 查询平均工资最低的部门信息和该部门的平均工资
- 查询平均工资最高的job信息
- 查询平均工资高于公司平均工资的部门有哪些?
- 查询出公司中所有manager的详细信息
- 各个部门中最高工资和最低工资的那个部门,最低工资是多少
- 查询平均工资最高的部门的manager的详细信息:last_name,department_id,email,salary
# 子查询经典案例
# 1. 查询工资最低的员工信息:last_name,salary
select last_name, salary
from employees e
where e.salary = (select min(salary) from employees);
# 2. 查询平均工资最低的部门信息
select *
from departments d
where d.department_id = (select e.department_id
from employees e
group by e.department_id
order by avg(e.salary)
limit 1);
# 3. 查询平均工资最低的部门信息和该部门的平均工资
select *
from departments d
inner join (select e.department_id, avg(e.salary)
from employees e
group by e.department_id
order by avg(e.salary)
limit 1) a
on d.department_id = a.department_id;
# 4. 查询平均工资最高的job信息
select *
from jobs j
where j.job_id = (select e.job_id
from employees e
group by e.job_id
order by avg(e.salary) desc
limit 1);
# 5. 查询平均工资高于公司平均工资的部门有哪些?
select department_id, avg(salary)
from employees e
group by e.department_id
having avg(salary) > (select avg(salary) from employees);
# 6. 查询出公司中所有manager的详细信息
select distinct m.*
from employees e
inner join employees m
on e.manager_id = m.employee_id;
# 7. 各个部门中最高工资中最低的那个部门,最低工资是多少
select max(e.salary),e.department_id
from employees e
group by e.department_id
order by max(e.salary) limit 1;
# 8. 查询平均工资最高的部门的manager的详细信息:last_name,department_id,email,salary
select e.*
from departments d
right join (select e.department_id, avg(e.salary)
from employees e
group by e.department_id
order by avg(e.salary) desc
limit 1) s
on d.department_id = s.department_id
left join employees e on e.employee_id = d.manager_id;
分页查询
语法:
select 查询列表
from 表
【join typejoin 表2
on 连接条件
where 筛选条件
group by 分组字段
having 分组后的筛选
order by 排序的字段】
limit offset,size;
- offset:要显示条目的起始索引(从0开始)
- size:要显示的条目个数
特点:
-
limit语句放在查询语句的最后,执行顺序也是最后
-
公式:
要显示的页数page,每页的条目数size
select 查询列表
from 表
limit (page-1)*size,size;
# 分页查询
# 案例1:查询前五条员工信息
use myemployees;
select *
from employees
limit 0,5;
select *
from employees
limit 5;
# 案例2:查询11-25条
select *
from employees
limit 10,15;
# 案例3:有奖金的员工信息,工资降序,前10名
select *
from employees e
where e.commission_pct is not null
order by e.salary desc
limit 10;
union联合查询
union:联合、合并,将多条查询语句的结果合并成一个结果;
语法:
查询语句1
union【all】
查询语句2
union【all】
......
应用场景:
要查询的结果来自于多个表,且多个表没有直接的连接关系,但查询的信息一致的时候;
特点:
- 要求多条查询语句的查询列数是一致的;
- 要求多条查询语句的查询的每一列的类型和顺序最好一致;
- 使用union会去重,使用union all会保留;



评论区